|
 |
|
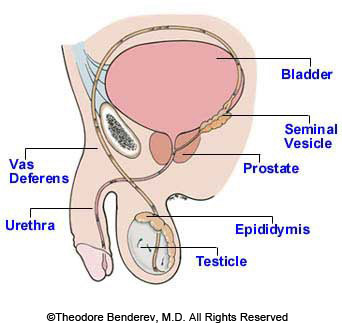
Anatomy and TermsTo understand Vasectomy, we should understand the basic terms for the anatomy of that region of the body: Testicle - one of two male reproductive glands that is the site of sperm and male hormone (testosterone) production. It is also known as the "Testis". Both testicles (or testes) lie within the scrotum. Epididymis - storage unit for sperm. Sperm also mature within this structure. There is one epididymis attached to the back side of each testicle, from where the epididymis also transports sperm to the vas deferens. Vas Deferens - a muscular tube (14 inch long by 0.1 inch wide) that propels sperm to the urinary tract. There are two of these. Each is also referred to as the "Vas" ("Vasa" is plural). Semen - a mixture of less than 1% sperm cells and 99% seminal secretions by volume. The volume of each ejaculate of semen is approximately 2 to 6 cc. Each cc of semen normally contains approximately 100 MILLION sperm cells. Seminal Vesicle - a gland that produces a component Prostate - another gland that contributes to seminal secretions. Bladder - a muscular, elastic pouch that serves to store and expel urine. Urethra - a passageway for semen and urine through the penis to the outside of the body. Other Vasectomy Terms:Vasectomy refers to: "Vas-" (or vas deferens) = one of the two small tubes for sperm transport. "-ectomy" = in this case, cutting and blocking off of the vas. A section of the vas may or may not be cut out. (Other examples of "-ectomy" include appendectomy and tonsillectomy). NSV = No-Scalpel Vasectomy Illustration by Tay McClellan, 1999, 2000.
|
Check out Theodore Benderev, MD on Yelp |
| Home | No-Needle, No-Scalpel Vasectomy | Anatomy & Terms | Risks & Complications | Alternatives | What to Expect | Vasectomy Procedure | Vasectomy Reversal | Dr. Benderev | Request an Appointment | Contact Us |
Site content copyright © 1999-2025 Theodore V. Benderev, M.D. All Rights Reserved. 1-888-VASECTOMY (888-827-3286) Notice of Privacy Practices The content of this site is provided for information only and not for medical advice. This site makes no claims as to the accuracy of its information and is not a substitute for direct consultation with your health care professional. Dr. Ted Benderev is a well known urologist since the1990's who has performed more than 15,000 vasectomy and vasectomy reversal procedures. His practice is conveniently located in the Orange County communities including Aliso Viejo, Anaheim, Costa Mesa, Corona, Fountain Valley, Fullerton, Huntington Beach, Irvine, Ladera Ranch, Laguna Hills, Laguna Niguel, Mission Viejo, Newport Beach, Orange, Rancho Santa Margarita, San Juan Capistrano, Santa Ana, San Clemente, Tustin, Westminster, and adjacent Inland Empire counties of Riverside and San Bernardino, San Diego and Los Angeles. |